SERVICES
Meditation is the discipline of silence practised to calm the body, mind, soul and spirit. It is one of the most significant and important practices in the spiritual realm of the human being and is the one that brings about changes at the level of cognitive awareness. The origin of meditation lies in the origin of the Zen concept, which refers to the transmission of the light of Buddhist wisdom that occurs in silence.
Archaeologists have found figures and engravings in India dating back to 3000 BC, showing figures sitting in the classical meditation posture - Lotus Flower - so meditation is believed to be at least 5,000 years old. Philosophers and mystics of all ages agree that silence is the beginning of the highest knowledge.
Around the 6th and 5th centuries BC different forms of meditation developed in Taoist China and Buddhist India. The exact origin of Buddhist meditation has not been perfectly defined, although the first texts referring to meditation appear in the Pali Sutras, where the formula for salvation was listed following the four basic rules: observance of the rules of morality, contemplative concentration, knowledge and liberation.
Meditation can be practised individually or in a group, with group meditation practice generating the highest rate of personal empathy by enhancing individual energies, resulting in a different and very enriching experience.
"Meditation brings wisdom; lack of meditation leaves ignorance. Know well what leads you forward and what holds you back, and choose the path that leads to wisdom" (Buddha).
Some types of Meditation
There are many types of meditation, depending on the school or origin of it. In this section we will only refer to some examples of the most well-known types of meditation:
BUDDHIST MEDITATION
In Buddhist meditation, observation of oneself and the activities of the mind is practiced to learn not to identify with that whirlwind that takes the joy out of life in the present.
ZEN MEDITATION
It has its origins in Chinese tradition. It is also known as Zazen meditation, which means “Zen Sitting” or “Sitting Meditation.”
VIPASSANA MEDITATION
The objective of Vipassana meditation is self-observation and inner knowledge to achieve Nirvana.
MINDFULNESS MEDITATION
A new Western trend that attempts to detach the practice of meditation from any ideological or religious connotation. It consists of living with full attention to the present and achieving peace in this frenetic world, it is "mental training".
MEDITATION with MANTRAS
Mantras are a series of syllables, words or phrases that apparently have no meaning, but which according to yogic tradition connect us with virtues or divine energies. During meditation, these mantras are repeated in order to focus our mind and direct our attention.
TRANSCEDENTAL MEDITATION
Transcendental meditation is one of the types of meditation most studied by science for its innumerable benefits, but at the same time it is also one of the most criticized, perhaps because transcendental meditation is only taught in authorized centers that must have the approval of the Maharishi Mahesh Institute
YOGA MEDITATION
Among the types of meditation, we must highlight those that are associated with the tradition and practice of yoga, such as Chakra meditations, Kundalini Yoga, Kriya Yoga, Tantra, Pranayama or Nada Yoga.
TAOIST MEDITATION
The characteristic of this type of meditation is the generation, transformation and distribution of inner energy. Inner silence is the basis of Taoist meditation. It is about the silence that appears little by little and subtly as you advance in the practice of meditation.
VISUALIZATIONS
A type of meditation more suitable for beginners. It can help you understand a problem that resides in your subconscious. It is the way to bring to light what you want. There are many types of visualizations such as: positive thoughts, learning to forgive, discovering what you want, etc.
It is a natural healing system or technique for healing the spirit and therefore the body, through the channeling of vital energy with the hands.
Born at the beginning of the 20th century, its origin is in Japan, with the great Master Mikao Usui, born on the 15th of August 1865 in the Japanese province of Gifu. He married Sadako Suzuki and had two children. He died in Fukuyama on the 9th of March 1926. Throughout his life he held various official positions in his native Japan.
He was a person with great spiritual concerns. His interest focused on having a direct experience of the healing processes mentioned in Buddhist scriptures.
Mikao Usui Sensei understood that an enlightened or conscious person contributes a lot to everyday life and considered that: “if every house had a member who practiced Reiki, the world would be a different place.”
Traditional Japanese beliefs regarding health and wellness are very different from those in Western countries. For example, the Japanese term for being healthy “genki de” means being in the original “ki” (there is no literal translation, but the meaning is mind, spirit, soul or heart), which contrasts with the term for being sick “byôki” which means sick ki. Health is, therefore, a condition of the mind, and being healthy is the original state of the body.
Mikao Usui Sensei enunciated five principles or gokai that are actually universal behavioral patterns that help us on our path through life, guiding us and bringing us closer to spiritual evolution.
• Kyo dake wa Ikaru-na/ Just for today
• Kyo dake wa Shinpai suna / Let go of anger
• Kyo dake wa Gyo o hage me/ Leave the worry
• Kyodake wa Kansha Shite/ Do your homework with enthusiasm
• Kyodeke wa Hito ni shinsetsu ni/ Be grateful, be kind to everything
Today the World Health Organization (WHO) presents Reiki as one of the multidisciplinary health practices valid for care at the community level within the Health System.
Reiki has several levels, and those who study it must receive their education from a Master. Students can reach Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, and even Master level.
Reiki is in itself a very complete healing system and has treatments for various types of ailments such as: functional disorders of the nerves, disorders of the respiratory system, functional disorders of the digestive organs, the circulatory system, blood metabolism and of the urogenital tract, surgical wounds and functional skin disorders, childhood diseases, women's diseases and also contagious diseases.
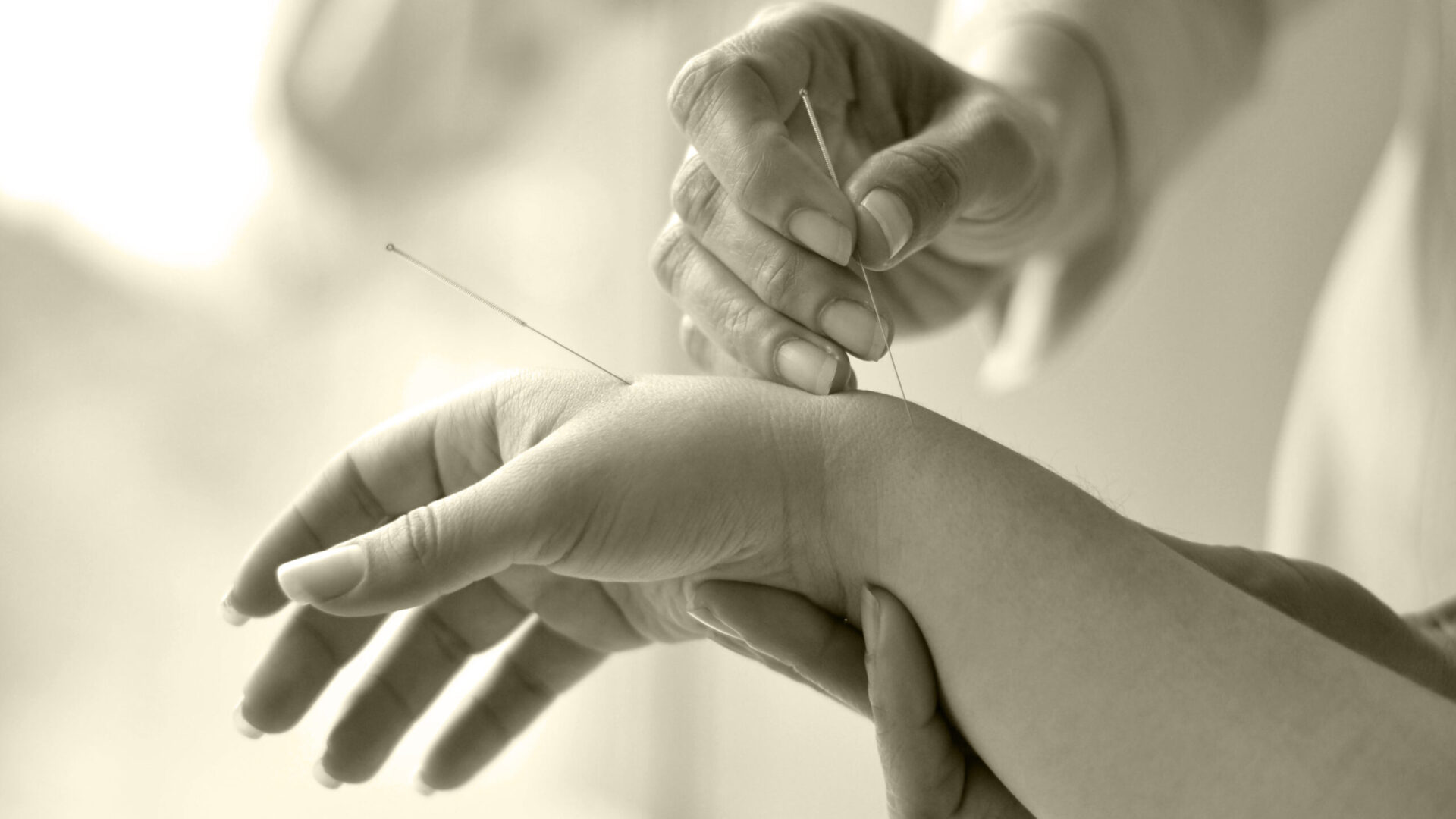
Traditional Chinese medicine is a precious legacy from five thousand years ago with a permanent projection in the present and maintains that the human body is a small universe united by channels of light through which Qi (energy) travels, and this taking into account that, when it comes to treating man for an illness, it is inevitable to treat his affective, emotional, psychological factors, etc., which are affecting his illness. Acupuncture and Moxibustion are the best known.
In Acupuncture, needles are inserted into certain points of these channels to restore the body's balance and try to cure and prevent illness. The needles are selected according to the conditions of the patient and are used to puncture the chosen points and stimulate them.
Stimulation of the points can also be done with Moxibustion, which is done by burning artemisia (moxa). It usually involves two modalities: a direct one, in which artemisia cones are applied to the selected points, and an indirect one, in which an artemisia stick is held at a certain distance from the surface of the body to heat the chosen area. The cones and sticks are made of dried mugwort leaves.
TERAPIA DE VENTOSAS
Cupping therapy has a long history in China dating back more than 2,000 years and is part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment. Data is found in ancient works from the Jin dynasty (265-420) in which applications with this method are already detailed. Its basic principle is the application of a suction cup on the skin, to which we will cause a vacuum effect, in order to improve the local vascularization of the area, thus allowing a greater flow of oxygen and nutrients in the affected area. Cupping can be used for any illness caused by cold wind and to stimulate the functionality of the autoimmune system. Nowadays it is also used aesthetically to reduce cellulite, fat and promote circulation that stimulates blood detoxification. Chinese cupping can relieve headaches, migraines, some skin problems (eczema, acne), the effects of stress, insomnia, or functional colopathies (constipation). Many patients who resort to this technique attest to its good results.
Defined as a discipline that offers non-pharmacological rehabilitation therapeutic treatment to diagnose, prevent and treat symptoms of multiple ailments, both acute and chronic. It is done through a set of methods, procedures, implements, of manual application.
Physical therapy is a safe and conservative approach, it has a preventive nature and is recommended for all those who want to enjoy good health, through the use of various techniques and exercises.
The lesser known benefit of physical therapy is that it helps manage age-related health problems by avoiding complex surgical procedures by preventing and controlling the physical deterioration of muscle strength, flexibility and joint mobility.
Knowing now that physical therapy not only serves to recover after an injury or illness, but also increases well-being, quality of life in general and helps you feel better without having to have a specific problem to correct. ¿Do you dare to include it in your preventive health routine?